Technofist
Internet of things (IOT) Projects and training for Engineering Students in Bangalore, iot ece projects
At TECHNOFIST we provide academic projects based on Internet of Things with latest IEEE papers implementation. Below mentioned are the list and abstracts on IOT domain. For synopsis and IEEE papers please visit our head office and get registered.
OUR COMPANY VALUES
Instead of Quality, commitment and success.
OUR CUSTOMERS
Are delighted with the business benefits of the Technofist embedded solutions.
IOT PROJECTS FOR FINAL YEAR
TECHNOFIST provides Latest IEEE transaction papers on IOT (Internet Of Things) based projects with latest IEEE concepts and training in Bangalore. We have 12 years experience in delivering IOT based projects with machine learning and artificial intelligence based applications with python and embedded coding. Below mentioned are few latest IEEE transactions on IOT related final year engineering projects.
Technofist is the best institute in Bangalore to carry out IOT based projects with machine learning and Artificial intelligence for final year academic project purpose. Latest IOT concepts for what is essential for final year engineering and Diploma students which includes Synopsis, Final report and PPT Presentations for each phase according to college format. Feel free to contact us for project ideas and abstracts.
Students of ECE, CSE, ISE, EEE and Telecommunication Engineering departments, willing to pursue final year project in stream of Embedded projects using IOT Internet of Things concept with EMBEDDED or Python coding implementation can download the project titles with abstracts below.
We also have few latest topics based on LORA WAN modules.
INTERNET OF THINGS
IoT (Internet of Things) is an advanced automation and analytics system which exploits networking, sensing, big data, and artificial intelligence technology to deliver complete systems for a product or service. These systems allow greater transparency, control, and performance when applied to any industry or system.
IoT systems have applications across industries through their unique flexibility and ability to be suitable in any environment. They enhance data collection, automation, operations, and much more through smart devices and powerful enabling technology.
IoT systems allow users to achieve deeper automation, analysis, and integration within a system. They improve the reach of these areas and their accuracy. IoT utilizes existing and emerging technology for sensing, networking, and robotics.
IoT exploits recent advances in software, falling hardware prices, and modern attitudes towards technology. Its new and advanced elements bring major changes in the delivery of products, goods, and services; and the social, economic, and political impact of those changes.
Here we provided a IOT/INTERNET things project list with abstract/ABSTRACT. IOT has been a very hot active during past few years and holds the potential as yet largely untapped to allow decision makers to track development progress using latest concepts. Latest IOT/INTERNET topics, Latest IOT/INTERNET concept for diploma, Engineering students, IOT/INTERNET project centers in Bangalore with high quality training and development.
Here is a list of project ideas for IOT/INTERNET concepts. Students belonging to third year mini projects or final year projects can use these projects as mini-projects as well as mega-projects. If you have questions regarding these projects feel free to contact us. You may also ask for abstract of a project idea that you have or want to work on. The own projects idea for diploma and Engineering students can also be done here.
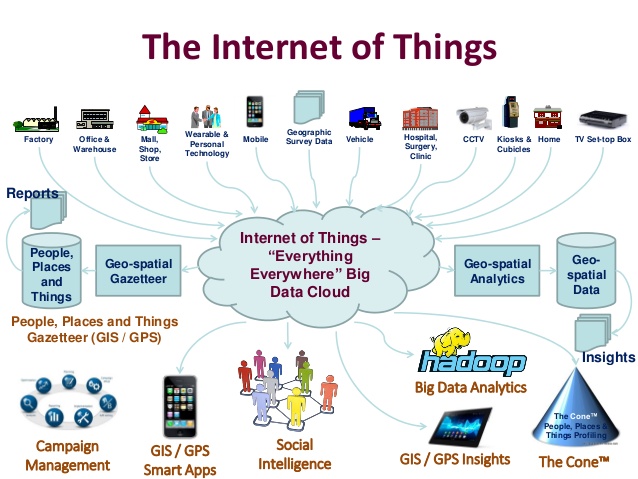
IOT FEATURES
The most important features of IoT include artificial intelligence, connectivity, sensors, active engagement, and small device use. A brief review of these features is given below :−
- AI: IoT essentially makes virtually anything “smart”, meaning it enhances every aspect of life with the power of data collection, artificial intelligence algorithms, and networks. This can mean something as simple as enhancing your refrigerator and cabinets to detect when milk and your favorite cereal run low, and to then place an order with your preferred grocer.
-
Connectivity: New enabling technologies for networking, and specifically IoT networking, mean networks are no longer exclusively tied to major providers. Networks can exist on a much smaller and cheaper scale while still being practical. IoT creates these small networks between its system devices.
-
Sensors: IoT loses its distinction without sensors. They act as defining instruments which transform IoT from a standard passive network of devices into an active system capable of real-world integration.
-
Active Engagement: Much of today’s interaction with connected technology happens through passive engagement. IoT introduces a new paradigm for active content, product, or service engagement.
-
Small Devices: Devices, as predicted, have become smaller, cheaper, and more powerful over time. IoT exploits purpose-built small devices to deliver its precision, scalability, and versatility.
IOT ADVANTAGES
The advantages of IoT span across every area of lifestyle and business. Here is a list of some of the advantages that IoT has to offer :−
- Improved Customer Engagement: Current analytics suffer from blind-spots and significant flaws in accuracy; and as noted, engagement remains passive. IoT completely transforms this to achieve richer and more effective engagement with audiences.
-
Technology Optimization: The same technologies and data which improve the customer experience also improve device use, and aid in more potent improvements to technology. IoT unlocks a world of critical functional and field data.
-
Reduced Waste: IoT makes areas of improvement clear. Current analytics give us superficial insight, but IoT provides real-world information leading to more effective management of resources.
-
Enhanced Data Collection: Modern data collection suffers from its limitations and its design for passive use. IoT breaks it out of those spaces, and places it exactly where humans really want to go to analyze our world. It allows an accurate picture of everything.
IOT SOFTWARE
IoT software addresses its key areas of networking and action through platforms, embedded systems, partner systems, and middleware. These individual and master applications are responsible for data collection, device integration, real-time analytics, and application and process extension within the IoT network. They exploit integration with critical business systems (e.g., ordering systems, robotics, scheduling, and more) in the execution of related tasks.
- Data Collection: This software manages sensing, measurements, light data filtering, light data security, and aggregation of data. It uses certain protocols to aid sensors in connecting with real-time, machine-to-machine networks. Then it collects data from multiple devices and distributes it in accordance with settings. It also works in reverse by distributing data over devices. The system eventually transmits all collected data to a central server.
-
Device Integration: Software supporting integration binds (dependent relationships) all system devices to create the body of the IoT system. It ensures the necessary cooperation and stable networking between devices. These applications are the defining software technology of the IoT network because without them, it is not an IoT system. They manage the various applications, protocols, and limitations of each device to allow communication.
-
Real-Time Analytics: These applications take data or input from various devices and convert it into viable actions or clear patterns for human analysis. They analyze information based on various settings and designs in order to perform automation-related tasks or provide the data required by industry.
-
Application and Process Extension: These applications extend the reach of existing systems and software to allow a wider, more effective system. They integrate predefined devices for specific purposes such as allowing certain mobile devices or engineering instruments access. It supports improved productivity and more accurate data collection.
IOT TECHNOLOGY AND PROTOCOLS
-
IoT primarily exploits standard protocols and networking technologies. However, the major enabling technologies and protocols of IoT are RFID, NFC, low-energy Bluetooth, low-energy wireless, low-energy radio protocols, LTE-A, and WiFi-Direct. These technologies support the specific networking functionality needed in an IoT system in contrast to a standard uniform network of common systems.
-
NFC and RFID: RFID (radio-frequency identification) and NFC (near-field communication) provide simple, low-energy, and versatile options for identity and access tokens, connection bootstrapping, and payments.
- RFID technology employs 2-way radio transmitter-receivers to identify and track tags associated with objects.
- NFC consists of communication protocols for electronic devices, typically a mobile device and a standard device.
- Low-Energy Bluetooth: This technology supports the low-power, long-use need of IoT function while exploiting a standard technology with native support across systems.
-
Low-Energy Wireless: This technology replaces the most power hungry aspect of an IoT system. Though sensors and other elements can power down over long periods, communication links (i.e., wireless) must remain in listening mode. Low-energy wireless not only reduces consumption but also extends the life of the device through less use.
-
Radio Protocols: ZigBee, Z-Wave, and Thread are radio protocols for creating low-rate private area networks. These technologies are low-power, but offer high throughput unlike many similar options. This increases the power of small local device networks without the typical costs.
-
LTE-A: LTE-A, or LTE Advanced, delivers an important upgrade to LTE technology by increasing not only its coverage, but also reducing its latency and raising its throughput. It gives IoT a tremendous power through expanding its range, with its most significant applications being vehicle, UAV, and similar communication.
-
WiFi-Direct: WiFi-Direct eliminates the need for an access point. It allows P2P (peer-to-peer) connections with the speed of WiFi, but with lower latency. WiFi-Direct eliminates an element of a network that often bogs it down, and it does not compromise on speed or throughput.
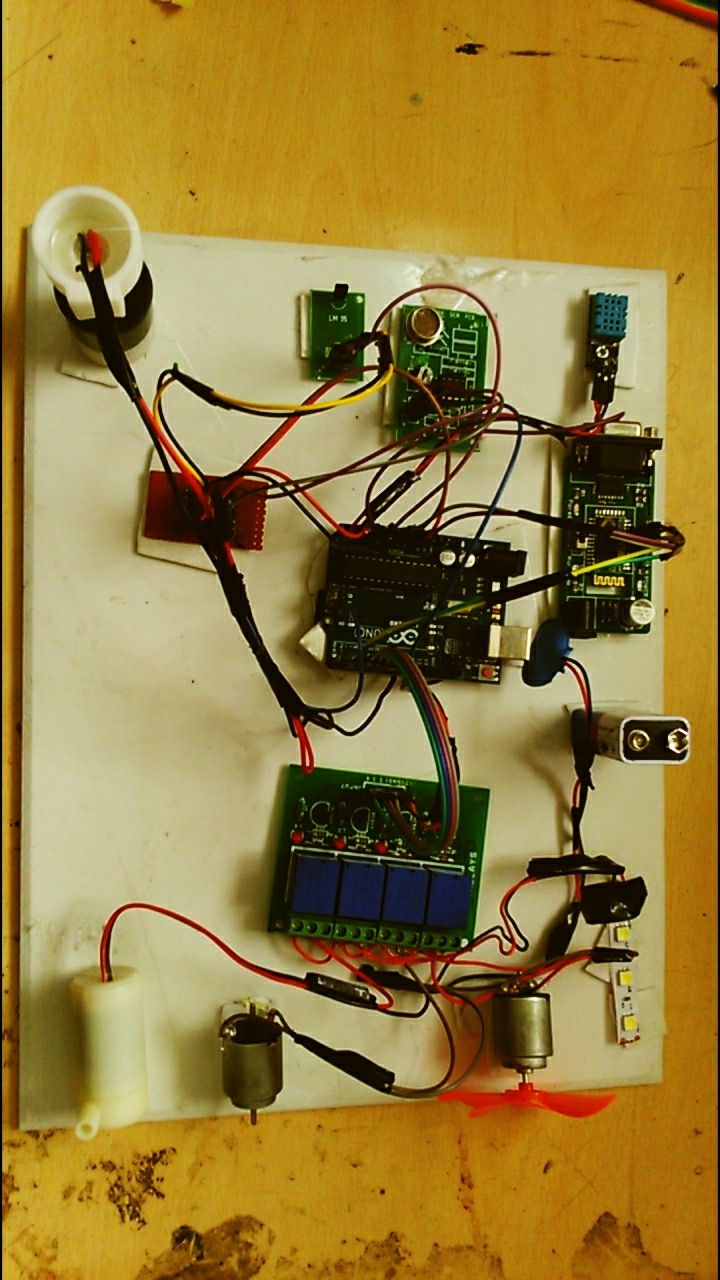
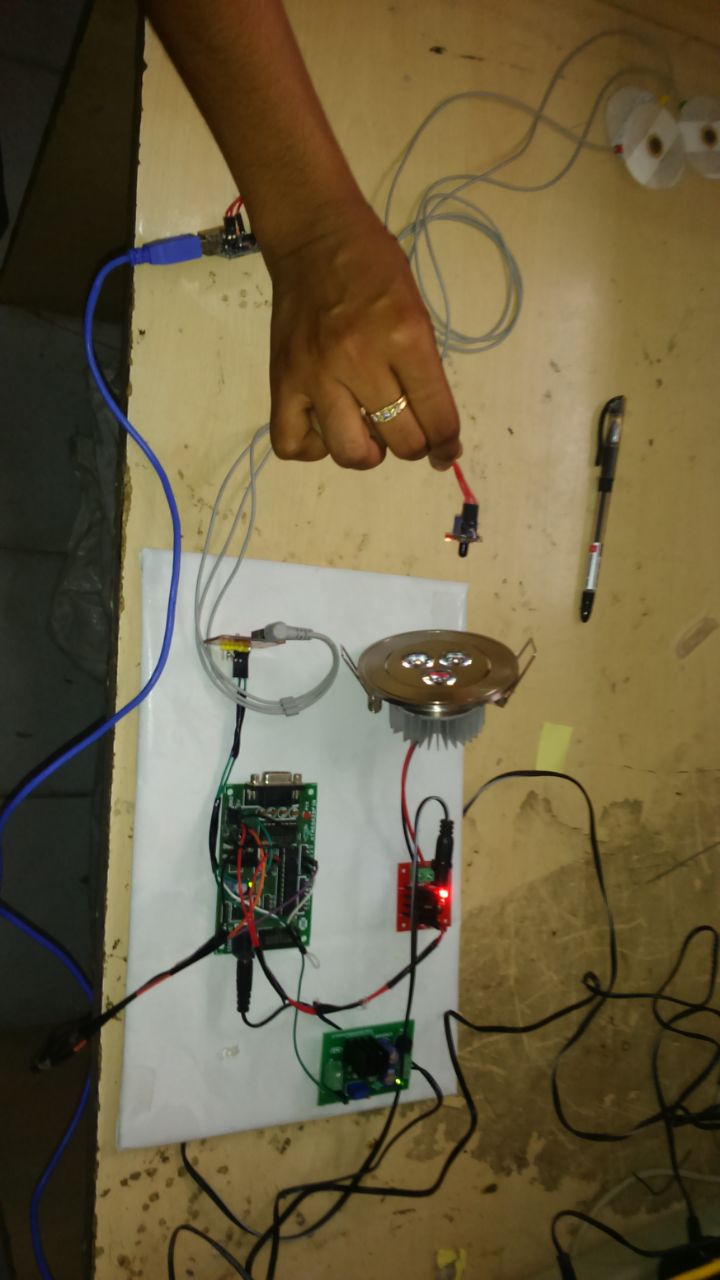
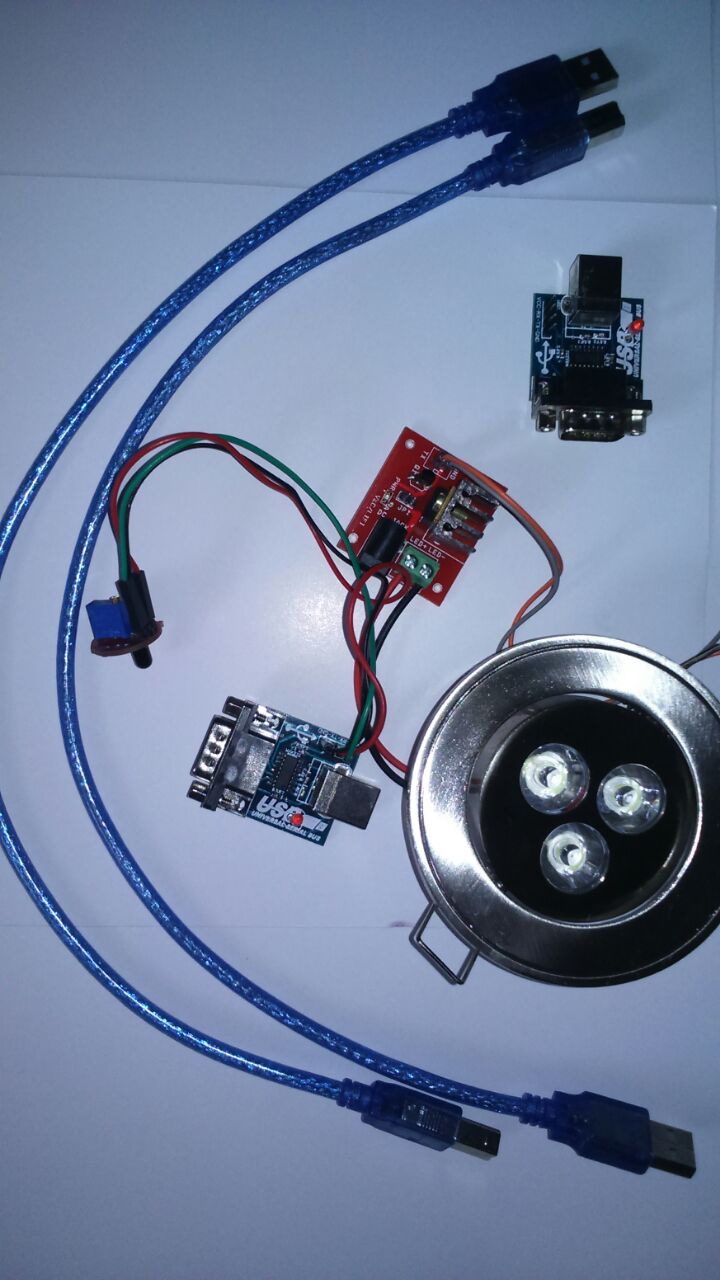
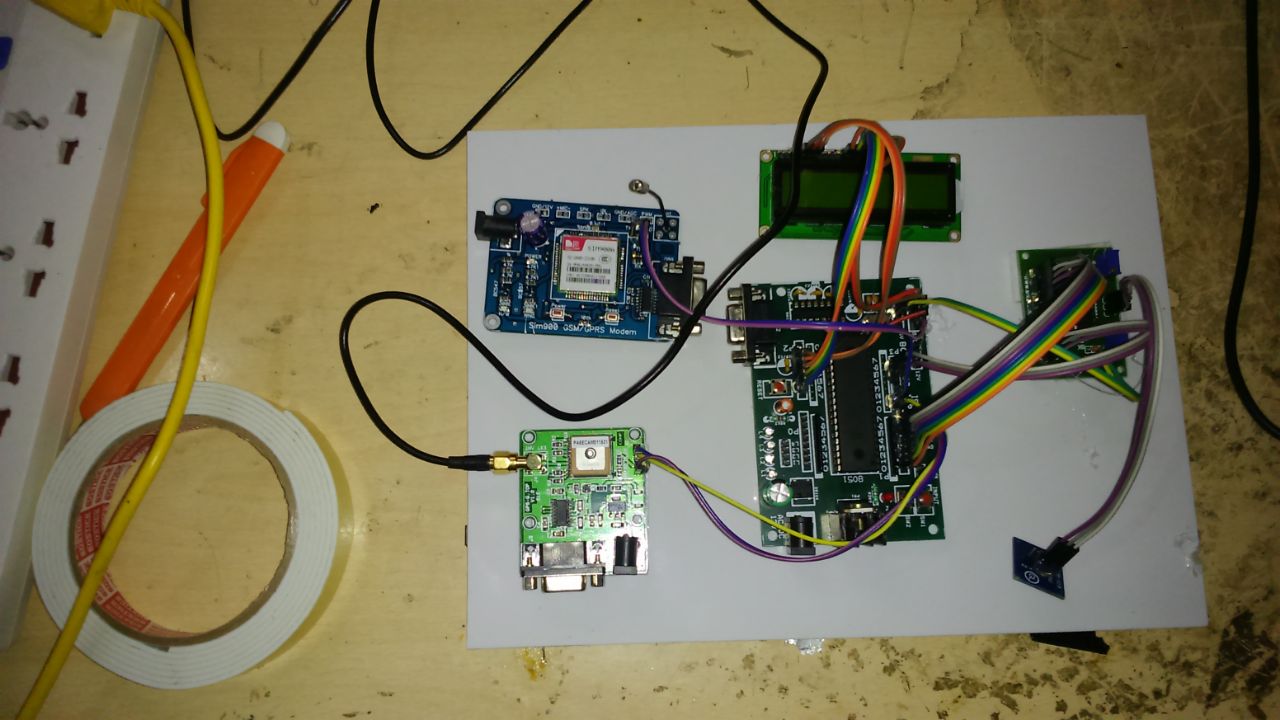
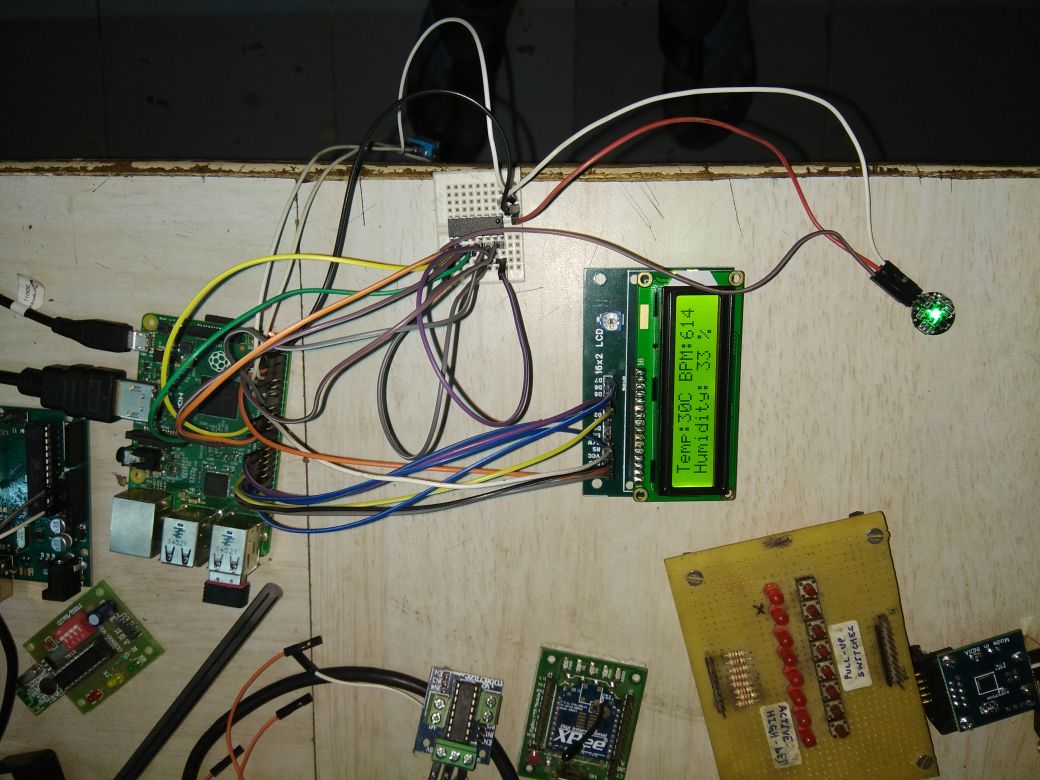
ACADEMIC PROJECTS GALLERY