TMO01
EFFICIENT FPGA MAPPING OF PIPELINE SDF FFT CORES
ABSTRACT - The FFT is one of the most widely used algorithms for calculating the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) owing to its efficiency in reducing computation time. Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) has been used in a wide range of applications, such as wide-band mobile digital communication system based on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) principle, where the system implementation is only feasible when the equipment complexity and power consumption are greatly reduced by utilizing a realtime FFT transformer to replace the bank of (de)modulators for each individual sub-carriers. FFT, as an efficient algorithm to compute the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT), is one of the most important operations in modern digital signal Processing and communication systems. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO02
IMPLEMENTATION OF SIXTH SENSE DEVICE
ABSTRACT - In this paper we present an approach for to create a Sixth Sense device which works of the principles of gesture recognition and image processing to capture, zoom(in and out) and toggle pictures with ease just by the help of colored caps/LED worn on the fingertips of the user. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO03
IMPLEMENTATION OF THREE LEVEL SECURITY SYSTEM
ABSTRACT - The potential threats coming from viruses, malware, adware and hackers are constant. The last couple of years have seen many massive global companies become hacked and compromised. In some cases, this has led to the theft of sensitive and private information including bank details, addresses etc. with a strong security system in place these intrusions can be stopped before they get anywhere near a company’s private data. This is not just important in terms of confidentiality but for avoiding the expensive fines that are imposed on companies that do not successfully protect customer’s data. The project is an authentication system that validates user for accessing the system only when they have input correct password. The project involves three levels of user authentication. There are varieties of password systems and authentications available. It contains three logins having three different kinds of systems. First one is given the access through the face recognition. Second type of authentication is scan the finger print of the user. By using these three level authentication, there is less chance for hacking. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO04
DESIGN OF AN 8-BIT PIPELINED RISC PROCESSOR DESIGN USING VERILOG HDL ON FPGA
ABSTRACT - This article describes an 8-bit RISC processor design using Verilog Hardware Description Language (HDL) on FPGA board. The proposed processor is designed using Harvard architecture, having separate instruction and data memory. The salient feature of proposed processor is pipelining, used for improving performance, such that on every clock cycle one instruction will be executed. Another important feature is that instruction set contains only 34 instructions, which is very simple, easy to learn and compact. The proposed processor has 8-bit ALU, Two 8-bit I/O ports, serial-in/serial-out ports, Eight 8-bit general-purpose registers, 4-bit flag register and priority based three vectored interrupts. Another advantage of the proposed processor is that it can execute programs with up to 262,144 instructions long, such that any practical programs can be fitted into it. The proposed processor is physically verified on Xilinx Spartan 3E Starter Board FPGA with 0.0517μs instruction cycle. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO05
DESIGN OF AN EFFICIENT ARCHITECTURE FOR DATA ENCRYPTION STANDARD BASED ON FPGA IMPLEMENTATION
ABSTRACT - To achieve the goal of secure communication, cryptography is an essential operation. Many applications, including health-monitoring and biometric data based recognition system, need short-term data security. To design short-term security based applications, there is an essential need of high-performance, low cost and area efficient VLSI implementation of lightweight ciphers. Data encryption standard (DES) is well-suited for the implementation of low-cost lightweight cryptography applications. In this paper, we propose an efficient VLSI archi3tecture for DES algorithm based encryption/decryption engine. Depending upon the encryption/decryption needs, the same set of architecture performs both encryption and decryption operations. In the implementation of DES algorithm, a chain of multiplexer-based architecture is used to implement the substitution operations (SBoxes). The proposed architecture is modeled in the VHDL design language and synthesized in the Xilinx Virtex-5 xc5vfx70t field-programmable gate array (FPGA) device. Hardware synthesis result shows that the proposed design utilizes only 1.07 % slice LUTs, 0.31 % slice registers and 29.22 % of bonded IOBs of the FPGA device fabric. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO06
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF CHANNEL EMULATOR FOR TESTING OF WIRELESS AIR INTERFACE USING VHDL
ABSTRACT - Experimental realism of wireless testbeds along with control and repeatability of experiments are some of the prominent fundamental barriers faced by researchers. To overcome these barriers, we are developing a wireless channel emulator that emulates the physical layer and brings about the realism and repeatability in our experiments. Channel emulators are generally used for testing air interface in Wireless Communication. In a laboratory test environment channel emulators replicate real world communication channel that exists between a transmitter and a receiver, it does so by providing a faded representation of the signal transmitted by the transmitter to the receiver inputs. It can be seen that emulator based approach helps us in understanding the performance of real world wireless channels. It also enables us to test our research in an operational wireless network, along with the advantages of a controlled experimental lab environment. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO08
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF 32-BIT FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER WITH CARRY LOOK AHEAD ADDER
ABSTRACT - A large number of computer applications(like Computer Graphics, Control Systems, Modeling System, Simulators etc.) needed floating point arithmetic. However, most of the presently available methods are slow and inefficient because of sequential design however the recent development in the field of programmable logic devices such as FPLA and CPLD opens the new area of parallel and high speed floating point designs. Considering that the synchronous architectures requires that that all clock events happen at the same time over the complete circuit which it not possible due to clock skew also the latency and throughput of the circuit are directly linked to the worst-case delay of the slowest element which increases the delay. Hence this paper presents self-timed carry look ahead adder based implementation of IEEE 754 32 bit floating point multiplier for FPGA devices. The simulation results shows that the proposed design has lower latency than synchronous design as well as lower power requirements. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO09
IMPLEMENTATION OF SELF RELIABILITY BASED WEIGHTED SOFT BIT FLIPPING AND DECODING FOR EG-LDPC CODES
ABSTRACT - Low density parity check(LDPC)codes were first discovered in 1960's Gallagher by and has received significant attention in these year 1990's because of their excellent performance when decoded using iterative decoders .EG_LDPC codes can be constructed using random or deterministic approaches. In this project, we focus on a sophisticated class of LDPC codes known as "EUCLIDEAN GEOMETRIC (EG)"_ LDPC codes using soft decision decoding. Minimum distance for EG_LDPC codes are also reasonably good and can be derived analytically. The decoded EG LDPC codes also seen then, it won't a have the serious error floors that plague randomly constructed LDPC codes. This fact can be explained by the observation made in that EG_LDPC codes do not have pseudo code words of weight smaller than their minimum distance.
LDPC codes can be decoded using hard decision and soft decision decoding methods. Hard decision decoding algorithm provide good performance but require high decoding complexity and are therefore those codes are not very suitable for high speed VLSI Implementations. We describe simple iterative decoders for low density parity check codes based on Euclidean Geometries, which are suitable for practical VLSI Implementations. In VLSI Implementation, applications very fast decoders are resuined which are using soft bit flipping decoding mechanism. In this project, the proposed SRWSBF decoder can achieve better error performance, low decoding complexity, and low power consumption. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO10
VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF LOW PASS FIR FILTER AND ANALYSIS USING MATLAB
ABSTRACT - In communication system digital filters plays a significant role as it provides high attenuation to the unwanted signals and at same time offers very low attenuation to the desired signals. In this paper, Low pass filter is designed using different window techniques namely Parzen, Nuttall and Rectangular. Here the Magnitude and phase response in time and frequency domain of these window techniques have been compared using MATLAB simulation. From the simulation result of different window, we found Nuttall window gives better magnitude and phase response as compared to other two techniques . Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO11
ARCHITECTURE IMPLEMENTATION OF DWT
ABSTRACT - In this paper, we presented the VLSI implementation and the simulation results of a systolic architecture for Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). This architecture is suitable for both decomposition and reconstruction of signals. The hardware utilization of the architecture is 100% unlike many other existing solutions in the literature. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO12
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FFT IP CORE
ABSTRACT - In this paper, an efficient mapping of the pipeline single-path delay feedback (SDF) fast Fourier transform (FFT) architecture to field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) is proposed. By considering the architectural features of the target FPGA, significantly better implementation results are obtained. This is illustrated by mapping an R22SDF 1024-point FFT core toward both Xilinx Virtex-4 and Virtex6 devices. The optimized FPGA mapping is explored in detail. Algorithmic transformations that allow a better mapping are proposed, resulting in implementation achievements that by far outperforms earlier published work. For Virtex-4, the results show a 350% increase in throughput per slice and 25% reduction in block RAM (BRAM) use, with the same amount of DSP48 resources, compared with the best earlier published result. The resulting Virtex-6 design sees even larger increases in throughput per slice compared with Xilinx FFT IP core, using half as many DSP48E1 blocks and less BRAM resources. The results clearly show that the FPGA mapping is crucial, not only the architecture and algorithm choices. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO13
FPGA DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF DIGITAL SWITCHING CONTROLLER FOR DC – DC CONVERTERS
ABSTRACT - DC-DC converters are electronic devices. It’s used whenever there is a need to change DC electrical power from one voltage level to another, in an efficient manner. Unlike an AC voltage DC cannot be just stepped down or stepped up. DC-DC convertor is DC equivalent to a Transformer. Typical applications of DC-DC converters are where 24V (which is used for a 24V device) DC must be stepped down to 12V DC to operate a 12V device. Similarly 12V-3V DC & 5V-2V conversion. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO14
VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF A SINGLE – CYCLE PROCESSOR FOR A SUBSET OF THE MIPS ARCHITECTURE IN VERILOG HDL (HARDWARE DESCRIPTION LANGUAGE)
ABSTRACT - Because of rich applications, smart operating systems on cell phones are now being migrated to home appliances like televisions. However, applications that are originally designed to be operated by touch screen are not suitable for televisions with these systems. This paper presents a method to manipulate applications with infrared remote control instead of touch screen on televisions without rewriting the code of these applications or adding extra expense on hardware. The principle of the method is to map keystroke events on the remote control to virtual touch based events according to specific mapping relationship corresponding to each application. Since the mapping relationship is various in each scene within one application, scenes should be recognized with feature information before the mapping process. The feature information and the mapping relationship in each scene have been set up prior to running of the application. When one application is running, the current scene of the application could be identified by scene recognition algorithm, the mapping relationship related to the current scene is able to be acquired, and then keystrokes on the remote control would be mapped to touch based events. The proposed method is tested on a smart television platform, and the result indicates the method can operate most applications by remote control, while the input response delay brought by the event mapping is negligibly less than one millisecond. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO15
VISUAL INSPECTION AND CRACK DETECTION OF RAILROAD TRACKS
ABSTRACT - Surface analysis is a very important measurement for track maintenance for Railroad Tracks, because deviations in surface geometry indicate where potential defects may exist. A rail surface defects inspection method based on computer vision system is proposed in the paper. Various algorithms related denoising, filtering, thresholding; segmentation and feature extraction are applied for processing the images of Railroad surface defect and cracks. It has mostly been implemented on computers. For better speed and complexity, the algorithms need to be implemented on embedded platforms. These methods were designed for MATLAB library. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO16
AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF INTRACARDIAC MASSES IN ECHOCARDIOGRAPH BASED ON SPARSE REPRESENTATION
ABSTRACT - Identification of intracardiac masses in echocardiograms is one important task in cardiac disease diagnosis. To improve diagnosis accuracy, a novel fully automatic classification method based on the sparse representation is proposed to distinguish intracardiac tumor and thrombi in echocardiography. First, a region of interest is cropped to define the mass area. Then, a unique globally denoising method is employed to remove the speckle and preserve the anatomical structure. Subsequently, the contour of the mass and its connected atrial wall are described by the K-singular value decomposition and a modified active contour model. Finally, the motion, the boundary as well as the texture features are processed by a sparse representation classifier to distinguish two masses. Ninety-seven clinical echocardiogram sequences are collected to assess the effectiveness. Compared with other state-of-the-art classifiers, our proposed method demonstrates the best performance by achieving an accuracy of 96.91%, a sensitivity of 100%, and a specificity of 93.02%. It explicates that our method is capable of classifying intracardiac tumors and thrombi in echocardiography, potentially to assist the cardiologists in the clinical practice. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO17
FAST AND ADAPTIVE DETECTION OF PULMONARY NODULES IN THORACIC CT IMAGES USING HIERARCHICAL VECTOR QUANTIZATION
ABSTRACT - Computer-aided detection (CADe) of pulmonary nodules is critical to assisting radiologists in early identification of lung cancer from computed tomography (CT) scans. This paper proposes a novel CADe system based on a hierarchical vector quantization (VQ) scheme. Compared with the commonly-used simple thresholding approach, the high-level VQ yields a more accurate segmentation of the lungs from the chest volume. In identifying initial nodule candidates (INCs) within the lungs, the low-level VQ proves to be effective for INCs detection and segmentation, as well as computationally efficient compared to existing approaches. False-positive (FP) reduction is conducted via rule-based filtering operations in combination with a feature-based support vector machine classifier. The proposed system was validated on 205 patient cases from the publically available online Lung Image Database Consortium database, with each case having at least one juxta-pleural nodule annotation. Experimental results demonstrated that our CADe system obtained an overall sensitivity of 82.7% at a specificity of 4 FPs/scan. Especially for the performance on juxta-pleural nodules, we observed 89.2% sensitivity at 4.14 FPs/scan. With respect to comparable CADe systems, the proposed system shows outperformance and demonstrates its potential for fast and adaptive detection of pulmonary nodules via CT imaging. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO18
CLOTHING COLOR AND PATTERN RECOGNITION FOR VISUALLY IMPAIRED PEOPLE
ABSTRACT - Choosing clothes with complex patterns and colors is a challenging task for visually impaired people. Automatic clothing pattern recognition is also a challenging research problem due to rotation, scaling, illumination, and especially large intraclass pattern variations. We have developed a camera-based prototype system that recognizes clothing patterns in four categories (plaid, striped, patternless, and irregular) and identifies 11 clothing colors. The system integrates a camera, a microphone, a computer, and a Bluetooth earpiece for audio description of clothing patterns and colors. A camera mounted upon a pair of sunglasses is used to capture clothing images. The clothing patterns and colors are described to blind users verbally. This system can be controlled by speech input through microphone. To recognize clothing patterns, we propose a novel Radon Signature descriptor and a schema to extract statistical properties from wavelet subbands to capture global features of clothing patterns. They are combined with local features to recognize complex clothing patterns. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, we used the CCNY Clothing Pattern dataset. Our approach achieves 92.55% recognition accuracy which significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art texture analysis methods on clothing pattern recognition. The prototype was also used by ten visually impaired participants. Most thought such a system would support more independence in their daily life but they also made suggestions for improvements. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO19
TRANSMISSION LINE FAULTS CLASSIFICATION USING WAVELET/FFT TRANSFORM
ABSTRACT - Power system fault identification using information conveyed by the wavelet analysis of power system transients is proposed for detecting types of transmission line faults. The work presented in this paper is focused on identification of simple power system faults. Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) analysis of the transient disturbance caused as a result of occurrence faults is performed. The maximum detail coefficient, energy of the signal and the ratio of energy change of each type of simple simulated fault are characteristic in nature and used for distinguishing fault types. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO20
LOSSLESS IMAGE COMPRESSION TECHNIQUE USING COMBINATION OF LZW AND BCH CODES
ABSTRACT - The development of multimedia and digital imaging has led to high quantity of data required to represent modern imagery. This requires large disk space for storage, and long time for transmission over computer networks, and these two are relatively expensive. These factors prove the need for images compression. Image compression addresses the problem of reducing the amount of space required to represent a digital image yielding a compact representation of an image, and thereby reducing the image storage/transmission time requirements. The key idea here is to remove redundancy of data presented within an image to reduce its size without affecting the essential information of it. We are concerned with lossless image compression in this paper. Our proposed approach is a mix of a number of already existing techniques. Our approach works as follows: first, we apply the well-known Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) algorithm on the image in hand. What comes out of the first step is forward to the second step where the Bose, Chaudhuri and Hocquenghem (BCH) error correction and detected algorithm is used. To improve the compression ratio, the proposed approach applies the BCH algorithms repeatedly until “inflation” is detected. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm could achieve an excellent compression ratio without losing data when compared to the standard compression algorithms. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO21
COMPLETE BLOOD CHECK USING IMAGE PROCESSING
ABSTRACT - The measure of WBC and RBC Cells are very important for the doctor to diagnose various diseases such as anaemia, leukaemia etc. So, precise counting of blood cells plays very important role. The old conventional method used in hospital laboratories involves manual counting of blood cells using a device called Haemocytometer. But this process is extremely monotonous, time consuming, and leads to inaccurate results. Even though hardware solutions such as the Automated Haematology Counter exits, they are very expensive machines and unaffordable in every hospital laboratory. In order to overcome these problems, this paper presents an image processing technique to detect and to count the number of red blood & white blood cells in the blood sample image using circular Hough transform and thresholding techniques. Detection and counting of blood cells have been done on three microscopic blood images of each patient which resulted in accuracy of 93.1%. The use of image processing technique helps in improving the effectiveness of the analysis in term of accuracy and time consumption. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO22
SLEEP DETECTION SYSTEM USING MATLAB IMAGE PROCESSING
ABSTRACT - The objective was to develop a non-invasive system for detecting the closing of eyes of a person driving an automobile and provide an alarm indication thus preventing road accidents from occurring. Live video relay of the driver's eyes is processed using Image Processing in MATLAB to detect whether the eye is closed for more than a fixed duration thus indicating conditions of fatigue, alcohol consumption etc. The system proves to be more accurate and safe compared to the existing sleep detection system developed using Infrared Sensors and Microprocessors. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO23
SMART ROOMS FOR POWER SAVING USING VIDEO PROCESSING
ABSTRACT - In this paper, we have developed a simple but totally real time people counter along with an automated device management system controlled by a digital circuit for ensuring proper power consumption. We have assumed a certain scenario by considering a particular space with predefined room capability , where not only the people’s entrance in that room is controlled by a counter and sensor system but also the room’s several electronic devices are controlled by a digital block circuit according to the number of people present in that room. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO24
IMPLEMENTATION OF VOICE BASED ACCESS CONTROL SYSTEM FOR HIGH SECURITY USING MATLAB
ABSTRACT - The speech processing and its application to intelligent system is the state of the art research. The systems are getting smarter day by day with the introduction of the speech signal to control the machine. The basic model of human speech system is used to design the algorithm which is able to detect words as well as an alphabetical letter to generate commands and can used for access control and security system. Once the speech is enhanced and the valued information is extracted, automatic speech recognition system is used to continuously detect the environmental sound and capture the portion of sound which is in the range of human speech frequency. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO25
MATLAB BASED EYE CONTROLLED WHEELCHAIR USING ARDUINO
ABSTRACT - Statistics suggests that there are around 40 cases per million of quadriplegia every year. Great people like Stephen Hawking have been suffering from this phenomenon. Our project attempts to make lives of the people suffering from this phenomenon simple by helping them move around on their own and not being a burden on others. The idea is to create an Eye Controlled System which enables the movement of the patient’s wheelchair depending on the movements of eyeball. A person suffering from quadriplegia can move his eyes and partially tilt his head, thus giving is an opportunity for detecting these movements. There are various kinds of interfaces developed for powered wheelchair and also there are various new techniques invented but these are costly and not affordable to the poor and needy people. In this paper, we have proposed the simpler and cost effective method of developing wheelchair. We have created a system wherein a person sitting on this automated Wheel Chair with a camera mounted on it, is able to move in a direction just by looking in that direction by making eye movements. The captured camera signals are then send to PC and controlled MATLAB, which will then be send to the Arduino circuit over the Serial Interface which in turn will control motors and allow the wheelchair to move in a particular direction. We also created a Fall Detection wherein a Person sitting on this automated wheel chair falls Buzzer will be generated using Accelerometer and warning message will be automatically send to concern Person. The system is affordable and hence can be used by patients spread over a large economy range. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO26
AUTOMATIC VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION BY NUMBER PLATE RECOGNITION
ABSTRACT - Automatic Vehicle Identification (AVI) has many applications in traffic systems (highway electronic toll collection, red light violation enforcement, border and customs checkpoints, etc.). License Plate Recognition is an effective form of AVI systems. In this project, a smart and simple algorithm is presented for vehicle’s license plate recognition system. The proposed algorithm consists of three major parts: Extraction of plate region, segmentation of characters and recognition of plate characters. For extracting the plate region, edge detection algorithms and smearing algorithms are used. In segmentation part, smearing algorithms, filtering and some morphological algorithms are used. And finally statistical based template matching is used for recognition of plate characters. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO27
CAMERA BASED COLOR IDENTIFICATION USING ROBOTIC ARM
ABSTRACT - Color is the most common feature to distinguish between objects, sorting, recognizing and tracking. Generally robot is mounted with a camera or the camera is mounted in the workspace to detect the object. This technology can be used in material handling in logistics and packaging industry where the objects moving through a conveyer belt can be separated using a colour detecting robot. In this paper the ‘Objrec’ algorithm is written in MATLAB for performing the operation. The ‘Objrec’ algorithm is executed to identify the object and send the appropriate commands to the microcontroller using serial communication for the robot to perform the sorting operation. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO28
AN IMPROVED MRI DENOISING ALGORITHM BASED ON WAVELET SHRINKAGE
ABSTRACT - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is very important in medical diagnosis. Denoising is a critical step for MRI diagnosis. Wavelet shrinkage is an efficient denoising method. It can be further classified into two types, the thresh-old method and the proportional-shrink method. However, both methods have their disadvantages. When the threshold method is implemented, the noise cannot be perfectly removed under a hard threshold while the denoised image may have fuzzy edges with a soft threshold. Furthermore, when the noise is too strong, the noise removal may not be enough by the threshold method. The proportional-shrink method requires that the variance field of the wavelet coefficients should change smoothly and the noise should obey a Gaussian distribution. If these assumptions are violated, the estimated ratios would not be precise so that too much texture information may be removed and the image can be distorted. This paper presents an improved method to combine the above two methods. By combining the processed results together, the improved method can achieve a good balance between denoising and retaining the texture information. We verify the efficiency of our method through some simulated data from an open database. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO29
IMPLEMENTATION OF FRUIT QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM BASED ON IMAGE PROCESSING
ABSTRACT - Non-destructive quality evaluation of fruits is important and very vital for the food and agricultural industry. The fruits in the market should satisfy the consumer preferences. Traditionally grading of fruits is performed primarily by visual inspection using size as a particular quality attribute. Image processing offers solution for automated fruit size grading to provide accurate, reliable, consistent and quantitative information apart from handling large volumes, which may not be achieved by employing human graders. This paper presents a fruit size detecting and grading system based on image processing. The early assessment of fruit quality requires new tools for size and color measurement. After capturing the fruit side view image, some fruit characters is extracted by using detecting algorithms. According to these characters, grading is realized. Experiments show that this embedded grading system has the advantage of high accuracy of grading, high speed and low cost. It will have a good prospect of application in fruit quality detecting and grading area. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO30
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON OF HYBRID WAVELET TRANSFORM-I VARIANTS AND CONTRAST LIMITED ADAPTIVE HISTOGRAM EQUALIZATION COMBINATION FOR IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
ABSTRACT - Image enhancement is one of the important part of image processing. Proposed research presents an image enhancement method, named CLAHE-HWT derived from its existing CLAHE-DWT, which combines the Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) with Hybrid Wavelet Transform Type I (HWT I) wavelets. The method includes, the original image is decomposed into low-frequency and high frequency components by HWT I. Then, the low-frequency coefficients is enhanced using CLAHE and the high-frequency coefficients kept unchanged to limit noise enhancement. Finally, the image is reconstructed by taking inverse HWT of the new coefficients. In order to counteract over-enhancement, the recreated and original images are averaged using an originally proposed weighting factor. Two orthogonal transforms combine to form a hybrid wavelet. Here different orthogonal transforms are used like Kekre, Walsh, Cosine, Hartley and Haar in 5 x 4 combinations total 20 hybrid wavelets of type I. This research compares all the 20 combinations of HWT I to find out the best combination of HWT with CLAHE. Experimental results demonstrate CLAHE-HWT shows better results for noise depression and avoid over enhancement. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO31
VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF DEEP NEURAL NETWORK USING INTEGRAL STOCHASTIC COMPUTING
ABSTRACT - he hardware implementation of deep neural networks (DNNs) has recently received tremendous attention: many applications in fact require high-speed operations that suit a hardware implementation. However, numerous elements and complex interconnections are usually required, leading to a large area occupation and copious power consumption. Stochastic computing (SC) has shown promising results for low-power area-efficient hardware implementations, even though existing stochastic algorithms require long streams that cause long latencies. In this paper, we propose an integer form of stochastic computation and introduce some elementary circuits. We then propose an efficient implementation of a DNN based on integral SC. The proposed architecture has been implemented on a Virtex7 field-programmable gate array, resulting in 45% and 62% average reductions in area and latency compared with the best reported architecture in the literature. We also synthesize the circuits in a 65-nm CMOS technology, and we show that the proposed integral stochastic architecture results in up to 21% reduction in energy consumption compared with the binary radix implementation at the same misclassification rate. Due to fault-tolerant nature of stochastic architectures, we also consider a quasi-synchronous implementation that yields 33% reduction in energy consumption with respect to the binary radix implementation without any compromise on performance. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981
TMO32
LIFI COMMUNICATION OF TEXT, AUDIO AND IMAGE
ABSTRACT - Li-Fi technology consist of transmission of data using light. So the proposed system has LED’s which is useful for data transmission and implement the basic concept of Li-Fi. It is divided into two modules Transmitter and Receiver.
Li-Fi is the term some have used to label the fast and cheap wireless-communication system, which is the optical version of Wi-Fi
. Contact: +91-9008001602 080-40969981



 Understanding the MATLAB Environment
Understanding the MATLAB Environment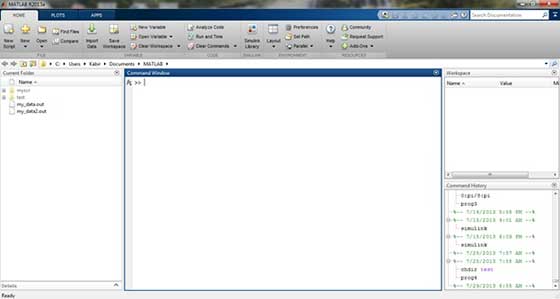 When MATLAB is started, the desktop appears in its default layout
When MATLAB is started, the desktop appears in its default layout 


